
How is it diagnosed?
- Endoscopy-Is a small flexible tube with a camera at the end used to visualise the gullet and the stomach. It is used to exclude the presence of a small cancer that can mimic the symptoms of Achlasia. It can also assess the size of the oesophagus and the tightness at the lower end.
- Barium Swallow. This investigation involves drinking a radio-opaque paste and a series of x-rays to analyse your swallowing and detect the areas of blockage. This can help determine the size of the oesophagus and the length of the narrowing in the oesophagus.
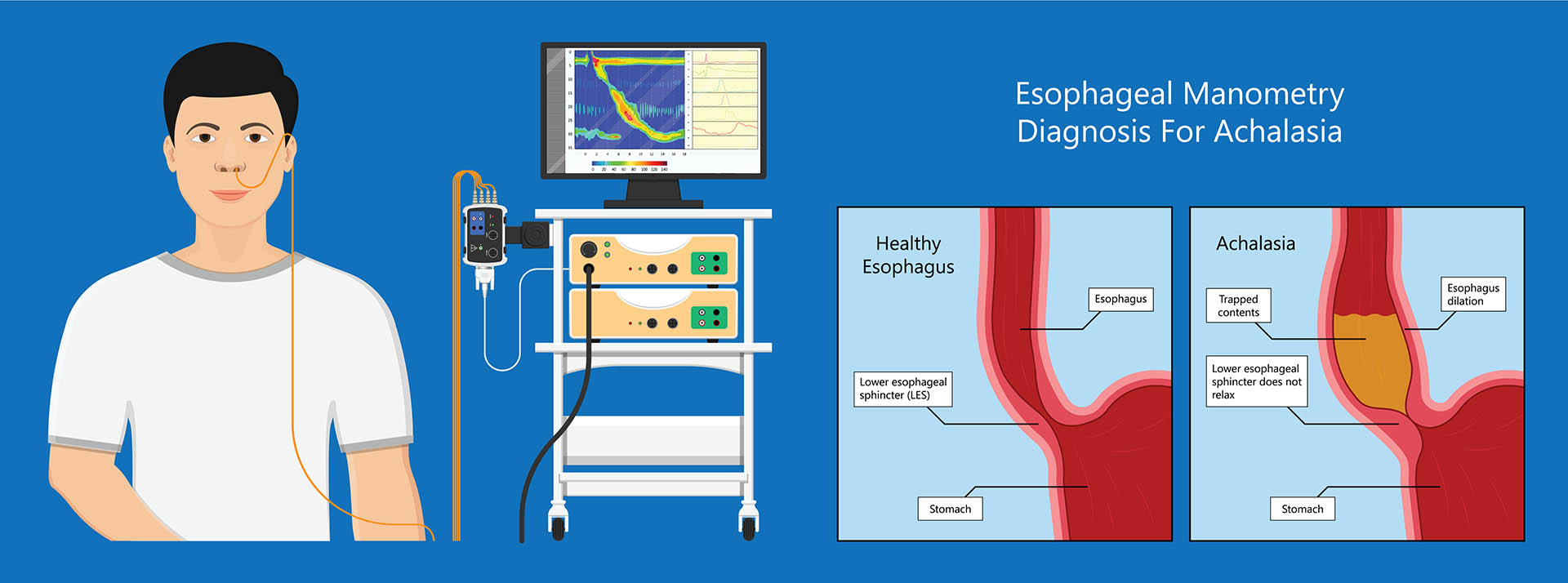
- Oesophageal Manometry: This test measures pressure waves in the oesophagus and is the main investigation for the diagnosis of achalasia by means of a small tube with pressure sensors. You will then be asked to take a few swallows of water while recordings are made. the pressures along your gullet and in the LOS.
What are the treatment options?
Unfortunately, treatments can’t actually cure the underlying process causing achalasia, although they can significantly help with symptoms by aiming to relax the sphincter so that food can pass into the stomach.
- Pneumatic Dilatation-This involves placing a pressure balloon in the area of the narrowing of the oesophagus usually under endoscopy or x-ray guidance and stretching. This will allow the muscles to stretch thus allowing the passage of food into the stomach. You might need repeated procedures with a 75% chance of success. The main complication is perforating the oesophagus which can make you seriously ill.
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox)– Botox is injected into the muscles of the LOS to paralyse them and relieve the spasm. This relaxes the muscles allowing food to pass through to the stomach. However, the effects may not be long-lasting and there is a very small chance of perforation (<1%).
- Endoscopy: New endoscopy therapies (e.g. POEM – per-oral endoscopic myotomy) are suitable for some patients as a permanent non-surgical treatment. These techniques are undertaken in specialist centres.
- Laparoscopic (keyhole) Surgery– This is the definitive treatment for Achlasia which gives a lasting effect. It involves dividing the muscles of the LOS thus relieving the obstruction and allowing passage of food into the stomach. A fundoplication procedure is performed to prevent the reflux of stomach contents as the muscles controlling this process are divided.





 Youtube Channel
Youtube Channel