

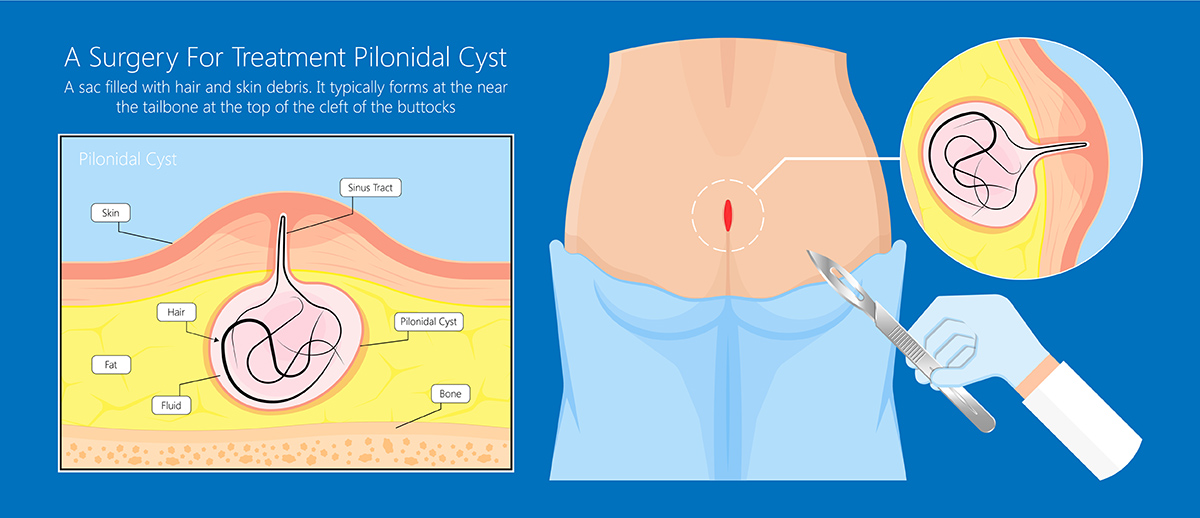
What are the treatment options?
- Antibiotics- Occasionally the infection can be controlled with a course of antibiotics but the rate of recurrence is high.
- Incision and Drainage- In case of acute infection when an abscess is formed it will need to be incised and drained under a general anaesthetic as an emergency.
- Wide Local Excision- This surgery involves excising a wide area of skin and surrounding tissue involving all the tracks and the residual defect is allowed to heal by itself. This involves repeated dressing changes over a 2 to 3 week period wherein the cavity slowly heals.
- Excision and Primary Closure- This involves excision of the skin and surrounding tissue involving all the tracts. The defect is then closed in a special way creating a flap shifting the midline cleft to one side and flattening the cleft. This reduces the healing time but is at a higher risk of wound breakdown and recurrence.
- Plastic reconstruction- The treatment in some recurrent cases can be very challenging and may need complex reconstruction flaps to facilitate healing of the area.





 Youtube Channel
Youtube Channel